
The global demand for seafood is skyrocketing, pushing aquaculture to the forefront of food production. This rapid growth calls for innovative, sustainable protein sources to support farmed fish.
Analysts predict that aquaculture will dominate seafood consumption by 2030, emphasizing the need for alternative feeds to address resource constraints.
Mealworms are stepping up as a game-changer. Packed with nutrients, they offer a sustainable protein solution. Their high digestibility and lower carbon footprint make aqua culture mealworms a promising alternative to traditional fishmeal.
Key Takeaways
- Mealworms are a good protein source for fish farming. They have lots of protein and are easy to digest, helping fish grow well.
- Adding mealworms to fish food helps their stomachs stay healthy. It also makes fish stronger and less likely to get sick.
- Using mealworms in fish farming is better for the planet. It cuts pollution and uses waste, supporting a reuse system.
Nutritional Composition of Aqua Culture Mealworms
Understanding the nutritional profile of aqua culture mealworms reveals why they are a powerhouse ingredient for aquafeeds. These tiny insects pack a punch when it comes to essential nutrients, making them a sustainable and effective alternative to traditional feed sources.
High Protein Content and Digestibility
Protein is the cornerstone of any aquaculture diet, and mealworms deliver it in abundance. With protein levels ranging from 13.68 to 22.32 grams per 100 grams, they rival and even surpass many conventional protein sources like beef and chicken.
| Nutrient | Content (per 100g) |
|---|---|
| Protein | 13.68–22.32 g |
| Fat | 8.90–19.94 g |
| Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids | Present |
| Zinc | High |
| Magnesium | High |
| Calcium | Low |
| Niacin | Present |
| Pyridoxine | High |
| Riboflavin | High |
| Folate | High |
| Vitamin B12 | High |
| Essential Amino Acids | Present |
| Comparison with Meats | Higher nutritional value than beef and chicken |
Mealworm protein is also highly digestible for many aquaculture species. Studies show that lower inclusion levels (5-10%) of mealworm meal in fish diets maintain excellent digestibility and nutrient uptake. This makes them an ideal choice for boosting growth without compromising feed efficiency.
Rich in Essential Amino Acids and Fatty Acids
Aqua culture mealworms are a treasure trove of essential amino acids (EAAs) and beneficial fatty acids. These nutrients are critical for fish growth, muscle development, and overall health. Mealworms contain 423 mg/g of EAAs, which make up about 50% of their total amino acid content. Arginine and leucine are the most abundant, supporting protein synthesis and energy production in fish.
| Component | Amount (mg/g) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Total Essential Amino Acids | 423 | Comprises about 50% of total amino acids |
| Arginine | 78 | Highest concentration among EAAs |
| Leucine | 62 | Second highest concentration |
| Methionine | 18 | Lowest concentration among EAAs |
| Total Non-Essential Amino Acids | 528 | Total amino acids in cells is 951 mg/g |
| Glutamic Acid | 219 | Highest among NEAAs |
| Tyrosine | 22 | Lowest among NEAAs |
| Oleic Acid | 31% | Dominant fatty acid in mealworms |
| Linoleic Acid | 28% | Second most abundant fatty acid |
| Palmitic Acid | 23% | Third most abundant fatty acid |
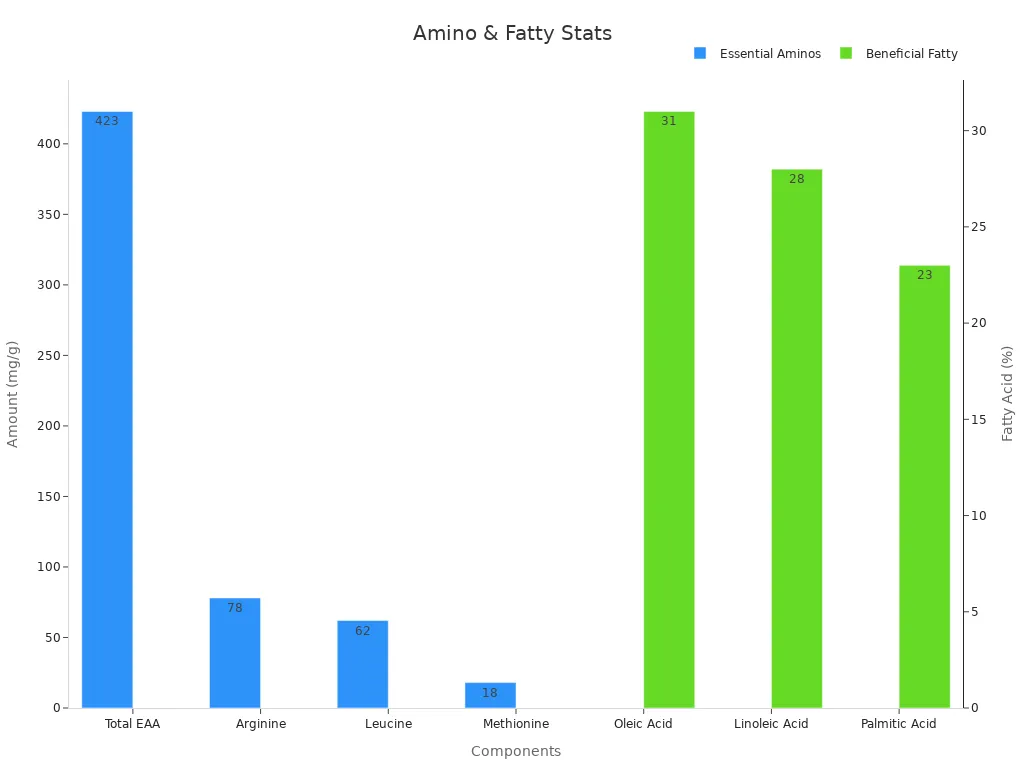
The fatty acid profile of mealworms is equally impressive. They are rich in oleic acid (31%), linoleic acid (28%), and palmitic acid (23%), which are vital for maintaining fish health and improving the quality of aquaculture products.
Presence of Vitamins, Minerals, and Probiotic Benefits
Mealworms are not just about protein and fats—they are also loaded with vitamins and minerals. They provide high levels of riboflavin, pyridoxine, folate, and vitamin B12, which are essential for metabolic processes and immune function in fish. Zinc and magnesium levels are also significant, contributing to bone health and enzymatic activities.
| Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Growth Performance | The inclusion of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with mealworms improved feed conversion ratio (FCR) and protein efficiency ratio (PER). |
| Intestinal Health | Probiotics in mealworms enhanced nutrient absorption and overall gut health. |
| Liver Health | Fish fed with mealworms showed better liver histology, indicating improved physiological functions. |
Additionally, mealworms offer probiotic benefits when combined with strains like Saccharomyces cerevisiae. These probiotics enhance gut health, improve nutrient absorption, and boost the immune system of fish. Healthier fish mean better growth rates and higher-quality aquaculture products.
Benefits of Aqua Culture Mealworms in Aquaculture
Enhanced Fish Growth and Feed Efficiency
Mealworms have proven to be a powerful ingredient for boosting fish growth and feed efficiency. Their high protein content and digestibility make them an ideal choice for aquafeeds. Studies show that including mealworms in fish diets significantly improves growth performance. Metrics like weight gain, specific growth rate, and feed conversion ratio (FCR) highlight these benefits. For instance, a dietary inclusion level of 14% mealworm resulted in better fish performance compared to traditional feeds. Even at higher inclusion levels, mealworms outperformed control diets, though optimal growth was observed at 14%.
Researchers also use statistical methods, such as ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple range tests, to measure these improvements. These tools confirm that mealworm-based feeds enhance feed utilization efficiency, ensuring fish grow faster while consuming less feed.
Improved Gut Health and Immune Function
Aqua culture mealworms contribute to healthier fish by improving gut health and strengthening immune systems. Their rich nutrient profile, combined with probiotic benefits, supports better digestion and nutrient absorption. When paired with probiotics like Saccharomyces cerevisiae, mealworms enhance intestinal health and boost immune responses. This combination reduces the risk of diseases, leading to healthier fish populations.
Additionally, mealworms contain essential vitamins and minerals, such as zinc and vitamin B12, which play a vital role in immune function. Healthier fish not only grow better but also require fewer medical interventions, making mealworms a cost-effective choice for aquaculture.
Positive Impact on Fish Quality and Market Value
Mealworm-based feeds improve fish quality, making them more appealing to consumers. Research on juvenile largemouth bass revealed that replacing fishmeal with mealworms enhanced growth performance and immune response. Fish fed with mealworms also showed significant improvements in body weight gain and feed efficiency. These benefits translate into higher-quality fish with better texture, flavor, and nutritional value.
From a market perspective, healthier and better-quality fish fetch higher prices. Farmers using mealworm-based feeds can achieve a competitive edge, as their products meet consumer demand for sustainable and nutritious seafood.
Environmental and Economic Advantages of Aqua Culture Mealworms

Reduced Carbon Footprint and Environmental Impact
Mealworm farming offers a sustainable alternative to traditional protein sources by significantly reducing environmental impact. Compared to livestock farming, mealworms require less land, water, and energy. Life cycle assessments (LCAs) highlight their eco-friendly nature through measurable metrics.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Global Warming Potential (GWP) | 20.4 kg CO2-eq |
| Non-Renewable Energy Use (NREU) | 213.66 MJ-eq |
| Agricultural Land Occupation (ALOP) | 22.38 m² |
| Terrestrial Acidification Potential (TAP) | 159.52 g SO2-eq |
| Freshwater Eutrophication Potential (FEP) | 12.41 g P-eq |
These figures show that mealworm production emits fewer greenhouse gases and uses less energy compared to traditional protein sources like fishmeal or soybean meal. By adopting mealworms in aquaculture, farmers can reduce their carbon footprint while contributing to a healthier planet.
Circular Economy Practices in Mealworm Farming
Mealworm farming aligns perfectly with circular economy principles. These insects can thrive on organic waste, such as vegetable scraps or agricultural by-products, turning them into high-quality protein. This process not only reduces food waste but also creates a closed-loop system where resources are reused efficiently.
Farmers can integrate mealworm farming into existing agricultural systems. For example, leftover crops or food waste can serve as feed for mealworms, which are then used as aquafeed. This approach minimizes waste and maximizes resource utilization. By incorporating mealworms into aquaculture, the industry can move closer to achieving a sustainable and circular economy.
Strengthened Food Security and Reduced Dependence on Fishmeal
Mealworms play a vital role in enhancing food security and reducing reliance on traditional feed sources like fishmeal. Studies show that mealworms can replace or partially replace fishmeal and soybean meal in livestock and aquaculture feeds.
| Evidence Description | Impact on Food Security and Fishmeal Dependence |
|---|---|
| Mealworms can replace or partially replace fish and soybean meal in livestock feed. | This reduces the EU’s dependence on imported feed, enhancing local food security. |
| Nutrient profile of mealworms is similar to fish and soybean meal. | Mealworms serve as a good alternative livestock feed, supporting sustainable protein sources. |
| Poultry diet studies show mealworms lead to similar or better growth performance. | This indicates that mealworms can effectively contribute to livestock productivity, further supporting food security. |
By reducing dependence on imported feed ingredients, mealworms help stabilize local food systems. Their nutrient-rich profile ensures that aquaculture species receive the necessary nutrients for growth and health. This makes aqua culture mealworms a reliable and sustainable protein source for the future.
Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability for Aquaculture
The economic viability of mealworm farming makes it an attractive option for aquaculture. Advancements in farming and processing technologies have improved production efficiency, making mealworm-based feeds more affordable. Regulatory support has also encouraged investment in insect farming, paving the way for large-scale commercialization.
Mealworms require fewer resources to produce compared to traditional protein sources. They consume less water, land, and energy, which lowers production costs. Additionally, their scalability ensures that farmers can meet the growing demand for sustainable aquafeeds. As global protein demand rises, mealworms offer a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution for aquaculture.
Mealworms are reshaping aquaculture by offering a sustainable and nutrient-rich alternative to traditional feeds. Studies show that guppies fed fermented mealworm diets grow faster and develop healthier guts, thanks to enhanced nutritional value and probiotics. This innovation supports better fish health and growth, making mealworms a transformative solution for aquaculture.
Globally, mealworm-based feeds address food insecurity and environmental challenges. Insects convert food waste into high-quality protein, reducing the need for water and land. With efficient farming methods, mealworms can scale production to meet rising protein demands. Encouraging further research and adoption will unlock their full potential in sustainable aquaculture.
Article author: Felix
FAQ
What makes mealworms a sustainable choice for aquaculture?
Mealworms consume less water, land, and energy. They also thrive on organic waste, turning it into high-quality protein. This reduces environmental impact and promotes sustainability. 🌱
Can mealworms replace fishmeal entirely in aquafeeds?
Mealworms can partially or fully replace fishmeal. Their nutrient profile supports fish growth and health, making them a reliable alternative for aquaculture diets.
Are mealworms safe for fish to eat?
Yes! Mealworms are highly digestible and packed with essential nutrients. Studies show they improve fish health, growth, and immune function.

